
Increasing availability of computerized decision support potentially decreases the resultant cognitive strain, but this remains a limitation. While not nearly as bad as the GRACE (Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events) Score, this decision instrument approaches the complexity limit for clinical acceptability.
In the original derivation and validation cohort, it was used in conjunction with zero-hour and two-hour troponin measurements to classify nearly 50 percent of the cohort as low risk, with a sensitivity greater than 99 percent. The advantage of this is greater specificity. Rather than each of the five elements being awarded up to two points, the EDACS breaks age, coronary disease, and signs and symptoms into myriad additive and subtractive elements. 6 This score incorporates many of the same elements seen in the HEART Score but at a more detailed and granular level. The next step in ED-centric decision-instrument development may come from New Zealand and Australia, with the Emergency Department Assessment of Chest Pain Score (EDACS). 4,5 At the same time, the number of patients classified as low risk increases to up to a third of the presenting cohort-an improvement that, by itself, ought to retire TIMI to its intended place on the inpatient side. When used as recommended by the authors, a HEART Score of 0 to 3 reflects a six-week event-free prognosis with a miss rate ranging between 0.6 percent and 1.8 percent in validation studies.

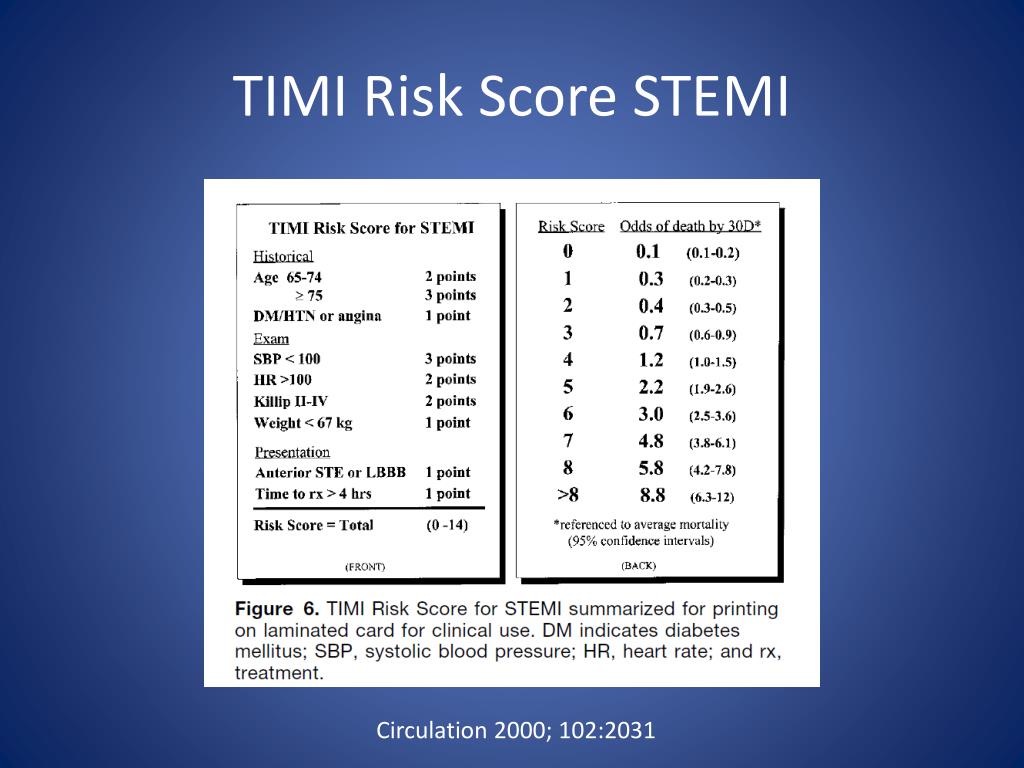
3 Reflecting several elements common to clinician gestalt, HEART demonstrates substantially improved performance over TIMI. From the Netherlands, the HEART (History, ECG, Age, Risk Factors, Troponin) Score was derived and designed for use in the emergency department. The development of these ED-centric decision instruments and disposition pathways indicate EM has moved beyond the hand-me-downs from cardiology.įortunately, science marches on. Pursuing this strategy is clearly foolish. 2 This strategy would result in 78 percent of patients being admitted for cardiac evaluation and still result in adverse outcomes for one in 50 discharged patients. As expected, the largest meta-analysis of prospective studies using TIMI in the emergency department demonstrated even requiring a TIMI of 0 for discharge is only 97.2 percent (95 percent CI, 96.4–97.8) sensitive for cardiac events. The generalizability of this cohort to our setting is simply lacking, and the logistic regression identifies elements-aspirin use within seven days-that may add specificity for poor outcomes in an intermediate- to high-risk cohort but fails in providing utility for describing a minimal-risk cohort. The original predictive value of the TIMI Score was intended to prognosticate 14-day mortality or new cardiac ischemia for cardiac inpatients, not emergency department presentations. These were patients admitted and anticoagulated for concerning chest pain in the setting of ECG changes, known coronary artery disease, or positive biomarkers. The original TIMI Score is not derived from an emergency department cohort. Fortunately for EM, but unfortunately for the brain cells sacrificially dedicated to its memory, the next wave of decision instruments promises to eliminate it from use. Numerous studies have utilized it, attempting to define a low-risk cohort from unselected chest pain patients presenting to the emergency department. Over the last decade, this score has been drilled, dogmatically, into many specialties, including emergency medicine. Many Patients Skip Prescribed Drugs After Myocardial InfarctionĮxplore This Issue ACEP Now: Vol 33 – No 04 – April 2014Ĭan you recite the elements of the TIMI Score-the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction Risk Score for Unstable Angina/Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction-from memory? 1 If you still can, it’s not surprising.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
